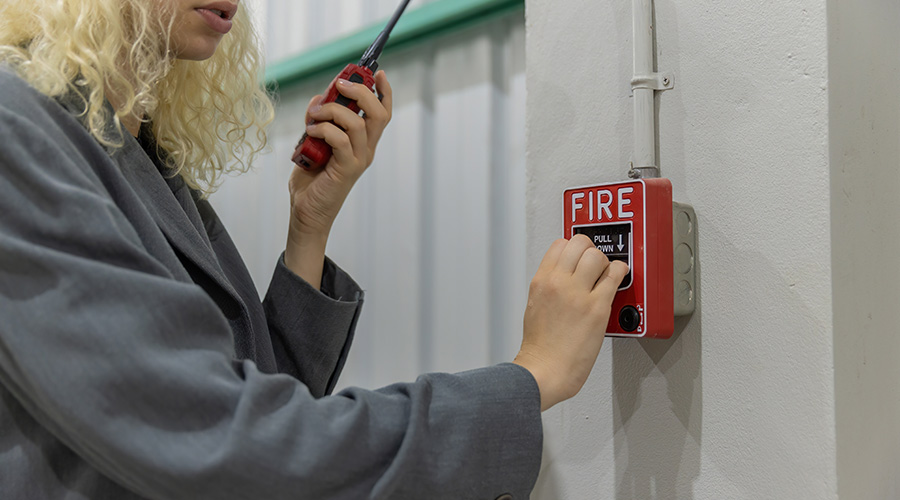
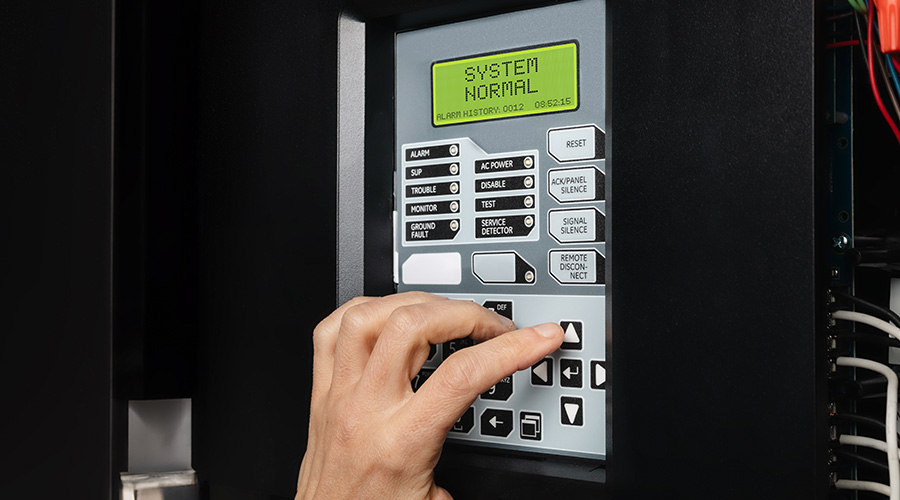
Fire Safety: Test Systems to Comply with NFPA 72
Technicians must test system components at the required intervals and with testing methods outlined in National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) Standard 72. Testing can help confirm a range of system functions and components, including:
- control-unit inputs and outputs
- battery capacity
- transmission equipment
- system wiring
- initiating devices
- alarm-notification appliances
- emergency-communications equipment and components.
Certain types of smoke and flame detectors also require special testing and calibration to verify they are operating within their listed and approved sensitivity ranges.
NFPA 72 also provides special testing criteria for heat detectors. For example, technicians must replace fixed-temperature, non-restorable, spot-type detectors after 15 years of use.
Another option is to have a laboratory test two detectors per 100 installed. If a failure occurs on any of the tested detectors, inspectors must remove and test more detectors to determine whether a general problem exists involving faulty detectors or a localized problem exists involving just one or two defective detectors.
Related Topics: